With the rapid development of industries such as the metaverse, digital twins, AR/VR, and film special effects, the demand for 3D digital content is experiencing explosive growth. However, traditional 3D modeling methods, characterized by high costs and low efficiency, have become a bottleneck for these industries. Consequently, mastering automated and intelligent 3D content generation technologies has become an urgent need and a practical necessity for researchers and engineers in related fields. This workshop focuses on the cutting-edge intersection of computer graphics, computer vision, and artificial intelligence, systematically introducing how to use advanced technologies like deep learning and neural rendering (e.g., NeRF) to automatically generate high-quality 3D models and scenes from images and videos. The workshop aims to systematically disseminate core knowledge, foster collaborative discussions on the latest frontiers and practical application scenarios of 3D content reconstruction and generation technology, and promote the prosperity of 3D content production.
Schedul
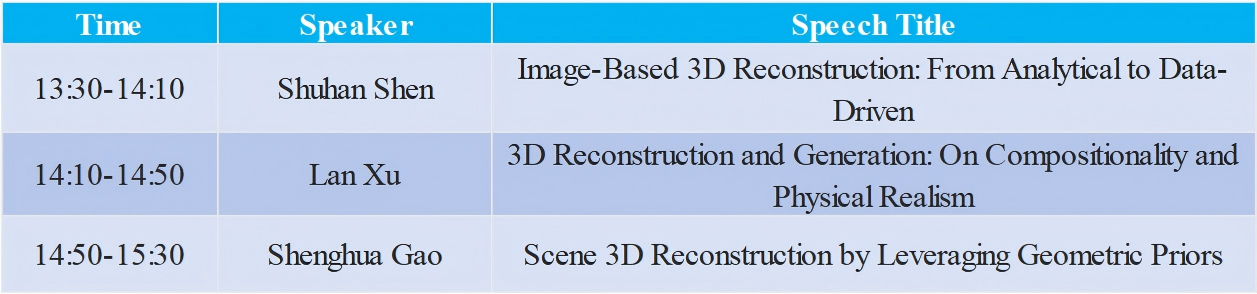
Oct. 31th 13:30 - 15:30
Organizer

Weiwei Xu
Zhejiang university, Professor
Biography:
Weiwei Xu is a Tenured Professor at the State Key Laboratory of CAD&CG, College of Computer Science and Technology, Zhejiang University, and a Chang Jiang Scholar (a distinguished honor appointed by the Ministry of Education of China). Previously, he served as a Postdoctoral Researcher at Ritsumeikan University, Japan, and as a Researcher in the Internet Graphics Group at Microsoft Research Asia. He also held the prestigious Qianjiang Scholar Distinguished Professorship at Hangzhou Normal University in Zhejiang Province. His primary research focuses on intelligent 3D perception, reconstruction, and simulation. He has published over 100 papers in high-level international academic conferences and journals, including more than 60 CCF-A classified papers in venues such as ACM Transactions on Graphics, IEEE TVCG, IEEE CVPR, and AAAI. He holds 15 authorized patents in China and the United States. The high-precision, high-fidelity 3D reconstruction technologies he developed have been applied in various industrial products and platforms, including Shining 3D's high-precision scanners, Baidu's Apollo autonomous driving simulation platform, Huawei's Cyberverse (Hetu), and XCMG's remote driving cockpit. In 2014, he was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Excellent Young Scientists Fund. He has led one Key Program of the NSFC and received a Second Prize of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Award.
Presenters

Shuhan Shen
Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Professor
Biography:
Shuhan Shen is a Professor at the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, an Adjunct Professor at the School of Artificial Intelligence, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Deputy Director of CAS Engineering Laboratory for Intelligent Industrial Vision. His research interest is 3D computer vision. He has published over 100 papers in leading journals and conferences in computer vision, photogrammetry and robotics, such as IEEE TPAMI/TIP, IJCV, ISPRS Journal, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, ICRA, and IROS. He has won four international competition championships in 3D vision at CVPR.. As project lead, he has overseen more than 20 research projects, including key projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, key projects of the Beijing Natural Science Foundation, Key R&D projects of Henan Province, and various enterprise R&D projects. He has received the 2023 Natural Science First Prize from the Chinese Association of Automation (Rank 3), 2023 Science and Technology First Prize from the Chinese Society for Surveying and Mapping (Rank 3), 2024 Scientific and Technological Progress First Prize from the Chinese Association of Automation (Rank 1)
Speech Title:Image-Based 3D Reconstruction: From Analytical to Data-Driven
Abstract:As a fundamental capability required for large-scale 3D scene reconstruction, Structure-from-Motion (SfM) aims to accurately and robustly recover camera spatial poses and intrinsic parameters from massive sets of 2D images The output of SfM not only serves as the basic input for subsequent 3D geometric reconstruction but is also a critical input for various neural rendering algorithms, including NeRF and 3DGS. The SfM problem itself represents a comprehensive application of traditional multi-view geometry theory, incorporating key concepts such as minimal configuration solutions, maximum likelihood estimation, and geometrically meaningful solutions. Despite decades of research, handling massive image data from large-scale, complex scenes still poses multiple challenges for SfM in terms of robustness, computational efficiency, and accuracy. This tutorial will examine representative geometric and neural solving methods for SfM over the past decade, analyzing the strengths and limitations of both analytical and end-to-end approaches, with the goal of outlining a viable technical pathway for large-scale Structure-from-Motion.

Lan Xu
Shanghai Science and Technology university, Researcher
Biography:
Dr. Lan Xu is an Assistant Professor, Researcher, and Doctoral Supervisor at the School of Information Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, where he also serves as the Director of the MARS Lab. His research focuses on computer vision, computer graphics, and computational photography, with a dedicated emphasis on the theory and technology of intelligent light field reconstruction. He primarily investigates the reconstruction and generation of dynamic and static scenes, volumetric video, neural rendering, and human-object interaction analysis. In recent years, he has led his team in developing a series of light field imaging systems. The resulting research has been published in top-tier journals and conferences such as ACM TOG, IEEE IJCV, IEEE TPAMI, SIGGRAPH, SIGGRAPH Asia, and CVPR. His work received two Honorable Mentions for the Best Paper Award at SIGGRAPH 2024 and won the Best Paper Award at SIGGRAPH 2025.
Speech Title: 3D Reconstruction and Generation: On Compositionality and Physical Realism
Abstract:The development of multimodal generative artificial intelligence has brought new breakthroughs in high-quality 3D content reconstruction, rendering, and generation, holding promise for future metaverse or human-computer interaction applications. This presentation will integrate our research team's progress in these areas, focusing on sharing novel approaches related to expression, composition, understanding, and interaction in 3D generation technology, and will analyze challenges and future directions.

Shenghua Gao
Hongkong university, Associate Professor
Biography:
Gaung-Hua Gao is a Tenured Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Assistant Dean at The University of Hong Kong. He is a recipient of the National "Thousand Talents Plan" Youth Project and the Shanghai Outstanding Academic Leader Program. His research interests include 3D and 4D reconstruction and generation, embodied artificial intelligence, and scientific AI. He serves as an Associate Editor for journals such as IEEE TPAMI, TMM, and TCSVT. His research work has been cited over 20,000 times (Google Scholar) with an H-index of 66.
Speech Title:Scene 3D Reconstruction by Leveraging Geometric Priors
Abstract:Three-dimensional reconstruction and generation technologies are the foundation of spatial artificial intelligence, enabling machines to perceive real-world spaces and create virtual environments, respectively. 3D reconstruction digitizes the physical world, helping machines understand environmental structures, object attributes, and spatial relationships. 3D generation allows machines to autonomously create diverse virtual scenes based on inputs such as text and images, widely used in training, simulation, and spatial design, thereby enhancing reasoning and innovation capabilities. These two technologies complement each other, collectively forming the "eyes" and "brain" of spatial AI. In this talk, I will share our latest research in 3D reconstruction and generation.

