- Frontiers of Machine Learning
- Multimodal Large Language Model and Generative AI
- Smart Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Analysis: From Perception to Interpretation
- 3D Imaging and Display
- Forum on Multimodal Sensing for Spatial Intelligence
- Brain-Computer Interface: Frontiers of Imaging, Graphics and Interaction
- Foundation Models for Embodied Intelligence
- Workshop on Machine Intelligence Frontiers: Advances in Multimodal Perception and Representation Learning
- Human-centered Visual Generation and Understanding
- Spatial Intelligence and World Model for the Autonomous Driving and Robotics
- Seminar on the Growth of Women Scientists
- Video and Image Security in the Era of Large Models Forum
- ICIG 2025 Competition Forum
- Visual Intelligence Session
With the rapid development of satellite constellations and advances in sensor technology, remote sensing technology is undergoing a major transformation from single-modal to multi-modal fusion. Remote sensing data has gradually evolved into a composite data stream encompassing multiple modalities such as optical, radar, hyperspectral, and LiDAR. Meanwhile, the development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, particularly deep learning and large models, has provided new tools for processing and analyzing these massive, heterogeneous multi-modal remote sensing data. Multi-modal remote sensing intelligence technology integrates multiple disciplines including computervision, remote sensingscience, deep learning, and geographic information systems (GIS), and is widely applied in fields such as military, meteorology, agriculture, geology, and environment. However, multi-modal remote sensing intelligence technology still faces multiple challenges, such as data alignment, model generalization, and computational efficiency. This forum intends to invite four renowned experts engaged in multi-modal remote sensing intelligence research from different fields as speakers to share their latest research progress in this area. Additionally, it will look forward to future exploration directions, build an interdisciplinary communication platform to break down domain barriers, inspire innovative thinking, and promote the advancement of multi-modal remote sensing intelligence technology.
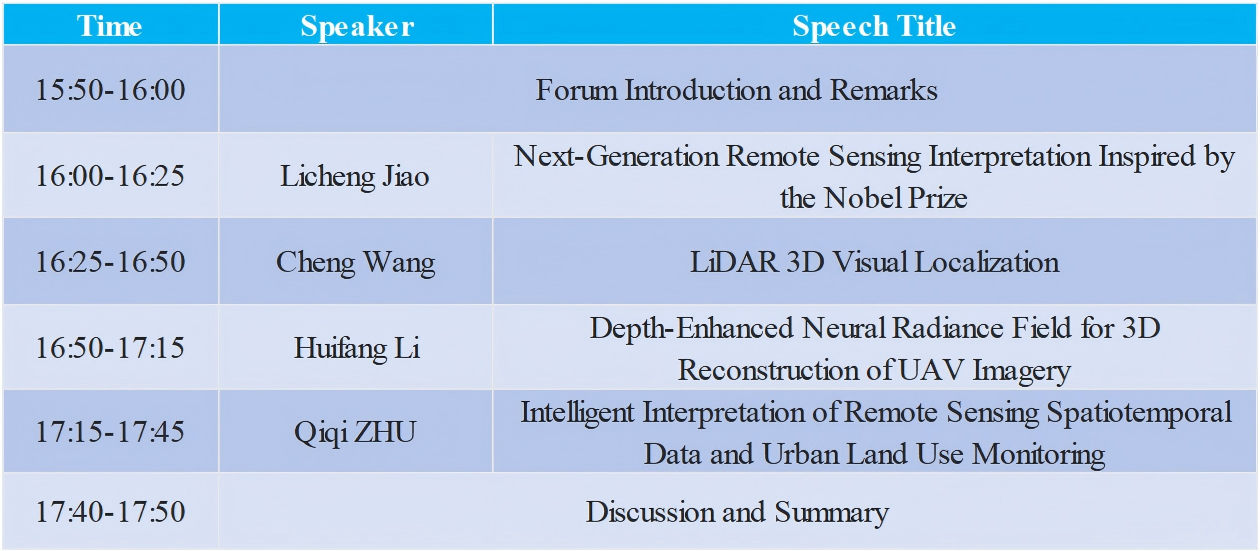
Schedul
Oct. 31th 15:50-17:50
Organizer

Kun Tan
East China Normal University, Professor
Biography:
Prof. Dr. Kun Tan is currently a Doctoral Supervisor of East China Normal University, Top young talents of the national "Ten Thousand People Plan", Deputy dean of School of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence and Deputy Director of Key Laboratory of Spatial-Temporal Big Data Analysis and Application of Natural Resources in Megacities (Ministry of Natural Resources). His main research interests comprise hyperspectral image processing, classification and change detection, spectral unmixing, surface parameter quantitative inversion and urban remote sensing. He has presided over more than 20 scientific research projects. He has published over 100 peer-reviewed journal papers, including ISPRS PE&RS, IEEE TGRS, JHM, PR, JAG etc.. He is associate editor of JAG, a Senior Member of IEEE and editorial board member of ISPRS PE&RS.

Lefei Zhang
Wuhan University, Professor
Biography:
Lefei Zhang is Vice Dean and Professor at the School of Computer Science, Wuhan University. He has previously served as a Visiting Scholar at University College London (UCL) and a Hong Kong Scholar at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. His research focuses on remote sensing information processing. He has published over 80 papers in IEEE Transactions and CCF A-class conferences, including 27 ESI Highly Cited Papers, with a total of more than 14,000 citations. He was awarded the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) and was selected as a Clarivate Highly Cited Researcher (2022-2024). He has presided over key, Excellent Young Scientists, and General Program projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC). He also led the team to win the Second Prize of Hubei Provincial Natural Science Award and the Second Prize of Natural Science Award of the Chinese Society of Image and Graphics. He currently serves as Chair of IEEE GRSS Wuhan Chapter and Associate Editor for journals such as IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS) and Pattern Recognition (PR). He supervised graduate students to win the championship of the 6th China Postgraduate Artificial Intelligence Innovation Competition.
Presenters

Licheng Jiao
Xidian University, Distinguished Professor
Biography:
Licheng Jiao, Academician of the European Academy of Sciences, IEEE Fellow, CSIG Fellow, Hua Shan Distinguished Professor at Xidian University, Dean of the Institute of Artificial Intelligence, Director of the Ministry of Education Key Laboratory for Intelligent Perception and Image Understanding, Member of the Discipline Panel of the Ministry of Education Science and Technology Commission, Pioneer Recipient of National Leading Talent Programs, Founding President of the Belt and Road Artificial Intelligence Innovation Alliance, Chair of the Shaanxi Provincial Artificial Intelligence Industry Technology Innovation Strategic Alliance, Vice President of CAAI (6th and 7th terms). He has been listed in Elsevier’s Most Cited Chinese Researchers List for eleven consecutive years. His main research interests include intelligent perception and image understanding, deep learning and brain-inspired computing, evolutionary optimization, and remote sensing image interpretation. He has received numerous honors and awards, including the Second Prize of the National Natural Science Award, the Wu Wenjun Artificial Intelligence Outstanding Contribution Award, the “Qiushi Artificial Intelligence Science and Education Award” for Outstanding Contribution, the title of National Model Teacher, and over ten provincial and ministerial-level First Prizes or higher in science and technology.
Speech Title: Next-Generation Remote Sensing Interpretation Inspired by the Nobel Prize
Abstract:As is well-known, the 2024 Nobel Prizes in Physics and Chemistry were awarded to AI researchers, which reveals the close connection between artificial intelligence (AI) and science & technology. The underlying reason lies in the efficient learning and optimization capabilities of neural networks. This presentation reviews the core technologies of AI and neural networks, introducing their connotations, development processes, as well as the transformations and challenges encountered during their evolution. Subsequently, aiming at the development difficulties of next-generation intelligent remote sensing interpretation, it puts forward insights and prospects ranging from basic theories to applied research.

Cheng Wang
Xiamen University, Professor
Biography:
Wang Cheng, Nanqiang Distinguished Professor at Xiamen University, recipient of national-level talent programs and grants, Fellow of IET, and Director of Fujian Key Laboratory of Urban Intelligent Sensing and Computing. His research interests include computer 3D vision, LiDAR, spatial intelligence, and smart cities.He has authored over 300 research papers published in prestigious journals and conferences such as Nature Communications, IEEE TPAMI, ISPRS-JPRS, IEEE TGRS, CVPR, NeurIPS, and AAAI. His work has been cited over 16,000 times on Google Scholar, with an h-index of 63. He serves as Chair of the ISPRS Working Group on Multi-Sensor Integration and Fusion, Founding Chair of CCF YOCSEF Xiamen, and Standing Council Member of the China Society of Image and Graphics (CSIG). His honors include the ISPRS Giuseppe Inghilleri Award, two First Prizes in Science and Technology Progress at provincial and ministerial levels, and one Special Prize for Teaching Achievement at the provincial level. He has chaired major academic events, including the 1st China Conference on 3D Vision (China3DV 2021), the 1st China Conference on Spatial Intelligence (ChinaSI 2025), and the China LiDAR Conference (ChinaLiDAR 2019).
Speech Title:LiDAR 3D Visual Localization
Abstract:Global navigation and positioning capability is a crucial cornerstone of the digital economy. However, due to obstructions such as urban buildings, bridges, tunnels, and indoor environments, as well as various potential interferences, satellite-based global positioning cannot meet the demands of applications like intelligent driving, internet of vehicles, and unmanned systems for all-weather, round-the-clock, and full-space positioning in urban areas. 3D laser scanning records the 3D spatial coordinates and sampling time of environmental surface points, making it one of the preferred sensors for 3D perception. With continuous advancements in power consumption, size, cost, and reliability of 3D laser scanning hardware, it has been widely adopted across multiple domains and is becoming a ubiquitous sensor with consumer-level applications and city-wide deployment. This talk will present our research on LiDAR-based 3D visual localization. First, the fundamental concepts of LiDAR visual localization will be introduced. Then, a fast LiDAR visual localization method based on deep regression will be discussed. Finally, the talk will focus on the development of LiDAR 3D localization based on implicit representations. The presentation will conclude with a summary of our efforts in the field of LiDAR visual localization.

Huifang Li
Wuhan University, Professor
Biography:
Her research focuses on urban remote sensing information processing and applications. She investigates theoretical and methodological frameworks—including physical modeling, statistical approaches, and deep learning—for correcting severe radiometric distortions in optical and thermal infrared remote sensing imagery caused by sensors, atmosphere, and complex surface conditions. Her work has been applied to multi-scale remote sensing monitoring and analysis of urban thermal environments. She has led four projects funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (including one Excellent Young Scientists Fund) and serves as the principal investigator of a key project under the National Key R&D Program. She has received several prestigious awards, including the First Prize of Science and Technology Progress of Hubei Province, the First Prize of Progress in Geographic Information Science and Technology, and the First Prize of Advancement in Surveying and Mapping Science and Technology.
Speech Title:Depth-Enhanced Neural Radiance Field for 3D Reconstruction of UAV Imagery
Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have shown great potential in 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis, but still face challenges in geometric accuracy and rendering quality in unbounded scenes. To address these issues, we propose a Bidirectional Depth and Space-optimized NeRF framework based on a multi-resolution hash encoding architecture. By integrating monocular depth estimation and dynamic space warping, our method enhances the modeling of distant objects and improves geometric consistency. It also improves training efficiency and rendering performance of NeRF in unbounded scenarios. Additionally, we construct an open-source UAV dataset covering multiple scene categories, enabling the evaluation of NeRF's generalization capability in complex environments, and further explored the prospects of 3D reconstruction by incorporating semantic information.

Qiqi ZHU
China University of Geosciences, Professor
Biography:
Dr. Qiqi Zhu is a Professor and Ph.D. supervisor at the School of Geography and Information Engineering, China University of Geosciences (CUG), and a selected "CUG Scholar" Outstanding Young Talent. His research focuses on intelligent extraction and analysis of large-scale remote sensing spatiotemporal data and its applications. He has published over 50 academic papers, with five first-authored articles recognized as ESI Highly Cited or Hot Papers. Dr. Zhu serves as an Associate Editor or Editorial Board Member for several SCI journals, including Geo-Spatial Information Science (GSIS) and IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters (GRSL). He is also a Senior Member of the IEEE.
Speech Title:Intelligent Interpretation of Remote Sensing Spatiotemporal Data and Urban Land Use Monitoring
Abstract:Urban areas are critical habitats for human survival. However, rapid urban expansion often leads to unregulated and excessive development, intensifying land scarcity, environmental degradation, and threats to arable land. This talk presents how the ECHO Lab leverages massive remote sensing spatiotemporal data to extract and analyze urban geoscientific information. Through advanced geospatial intelligence, the team aims to safeguard sustainable development of urban communities, ecosystems, and agricultural land. This work contributes to addressing key national strategic needs in urban planning, land management, and ecological protection.

